Power Consumption Is An Important Consideration
The future of self-driving is exciting, and as we dream about what tomorrow’s public roads will look like there are many promises beyond the horizon.
From the ability to travel without having to worry about poor driving conditions or reckless drivers causing a collision on the road, autonomous technology promises a brighter and safer future for everyone!
Many obstacles stand in the way of widespread adoption of this mode of transportation, but the ability for these vehicles to travel long distances in a convenient manner is one of the biggest concerns of consumers and automakers.
Having the ability to travel hundreds of miles between filling up or charging is a matter of convenience and practicality that faces autonomous car technology.
While the exact amount of electricity these cars will use is unclear, most experts agree that just the onboard equipment could consume up to 2,500 watts per second depending on the vehicle’s configuration. The power-consumption problem posed by autonomous cars was highlighted in a recent study conducted by the University of Michigan Center for Sustainable Systems.
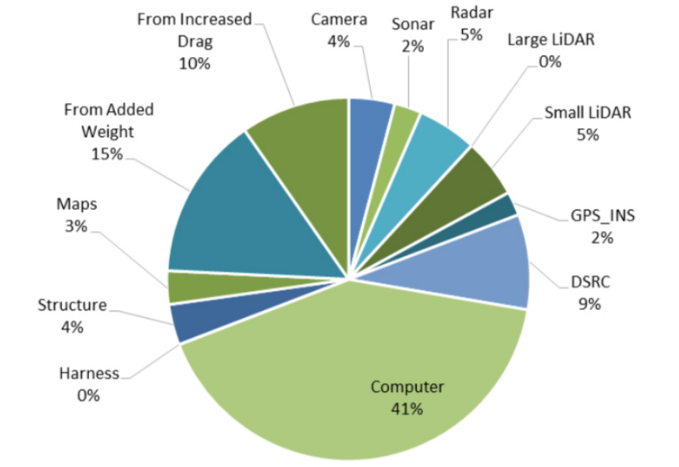
In this report, researches found that current models of autonomous cars will need to employ some aspects of battery-power for the viability of the long-term vision, but in the short-term manufacturers just do not have the means to make batteries the primary power source.
Battery Technology Is Not Ready For Autonomous Vehicles
Not only is current battery technology inefficient, but it also lacks storage capability that limits the range of vehicle operation. Modern day electric vehicles (EV) have a maximum range of 337 miles, but the distance an electronic vehicle can travel in a single charge varies greatly between different makes and models.
The average American drives between 30-40 miles each day so EV range can meet the needs of most consumers. However, the limited range of a few hundred miles per charge does not take into account the energy needed for onboard sensors, computers, and transmitters that autonomous cars will require.
Current EVs can handle daily use of driving between work and home, but today’s EVs are not able to transport consumers going on long road trips- especially since the cars must be recharged using specific charging ports and it can take time to complete each charge.
Ford’s Bet On Hybrid Autonomous Vehicles
Ford’s Vice President, James Farley, said in a recent interview with Automotive News that hybrid vehicles make the most sense for the future of automotive production because this type of car is the most profitable.
He said that Ford is looking to hybrid vehicles as the basis of their autonomous car strategy because this approach will reduce wasted time for owners when their vehicle is not transporting people or goods.
Essentially, Ford is betting on the fact that battery technology will improve but EVs need to rely on the convenient and proven gas-powered technologies to support autonomous cars in the near future.
Instead of relying on a cutting-edge technology that has not fully matured like battery-power, or a fuel method that has proven disadvantages for autonomous cars and the environment like gasoline, Ford is betting their short and mid-term success on hybrid self-driving vehicles so they can get the both of the two technologies.
Balancing User Functionality & Power Efficiency
Computers, GPUs, and sensors are among the leading technologies used by autonomous cars to navigate public roads. These systems are used to help computers interpret their surroundings, and the efficiency of these processors are the most critical elements for experts in the self-driving car industry.
Software and hardware companies are racing to find ways to make their products more potent while also reducing the amount of energy those systems use. As computer hardware companies like Nvidia work to improve the performance and efficiency of their products, they are able to work with the first-generation autonomous car manufacturers to implement the best solutions for each model.
Of course, battery-electric, gasoline powered, and hybrid propulsion are not the only options. There are other power options like Hydrogen fuel-cell technology that is starting to receive increased attention among some automakers.
This technology promises increased uptime and zero emissions. However, like all energy methods, Hydrogen fuel cells are not ready for large-scale manufacturing, and many logistical obstacles are preventing it from the wide-spread application.
Powering Vehicles Of The Future
Regardless of arguments from environmentalists, technologists, or politicians, the truth is that the future of the auto industry relies on electric power.
The auto industry can not bet on a single technology or power method based on current-day trends, and like history has proven we will need to take continual steps toward the future of the transportation industry!

